前言:
這是最近看 Paper 時看到的方法,有別於以往的先壓縮再加密,這是一個同時達到加密跟壓縮的方式,且概念相當簡單,只是運用簡單的亂數產生就能達成,非常聰明且漂亮的想法,特此介紹。
亂數:
標題有個關鍵字是 Chaos-Based,這個的意思就是使用亂數的方法來達成,大家都知道電腦中所謂的亂數其實並不是真正的亂數,而是 Pseudo Random,因為要讓電腦產生真正的亂數基本上不可能,連人自己要產生真正的亂數都不太可能了,更何況電腦,所以在電腦中實作亂數的方法就是找一些簡單的數學式子,這些式子帶出來的結果會無法預測,且跟初始條件或參數有極高的敏感性。意思就是是如果初始條件或參數差了一點點,但結果可能就會差的十萬八千里遠。電腦透過運算這樣的函數,來計算出要丟出來的亂數是多少。
在這裡我們使用的亂數產生是 Logistic Map,以下是他的式子,可以注意到它的運算非常簡單,要算出下一項只要透過簡單的乘法即可,不過要注意的是 r 需要在 3.6 ~ 4 之間較好,他還有一個好的特性是每一項都會在零跟一之間。
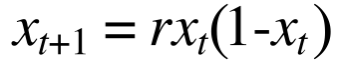
以下展示此函數的第100項到第110項的值,看起來很像還不夠亂的原因是還太前面了,通常都會取個1000項之後就看不太出來了。
演算法:
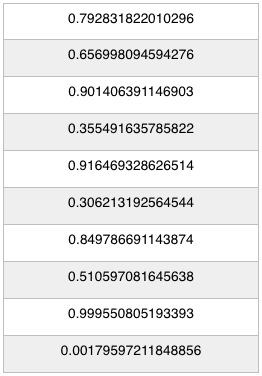
知道怎樣得到亂數之後,直接就進入他的想法吧,它主要的想法是先把一個區間切成好幾個小塊,每一塊有對應的數字等,機率高的符號,會佔比較多塊,相對的機率低得就比較少塊。並且用 Logistic Map 去產生亂數,看看產生出來的亂數對應的區塊是不是要的,如果不是就修正並重複剛剛的動作繼續往下對應,其中再找到對應之前所花的次數就是密文。因為機率高的符號,被對應到的機率也高,所以可以用比較少的次數對應到,相對的就是比較短的 bit 長度,而機率低的就會有比較長的 bit 數,達到壓縮效果。
相信到這裡大家還是不太明白,我們來看一個簡單的例子,假設A出現的機率是1/2,B是1/4,C跟D都是1/8,則整個區塊會被切成如下第一張圖,假設我們現在要找的是C,第一次運氣不好用 Logistic Map 產生的亂數落在A區塊,則把A改成除A之外最大機率的值,以例子來說是B,繼續下去,直到找到為止,找到之後這中間尋找的次數就是C加密過後的結果,以例子來說就是3。找完之後把整個區塊恢復原狀再繼續往下加密。
這個方法還有一些先天上的好處,比方說同一個字母會對應到不一樣的密文,因為亂數是一直取下去的,即使是同一個字元要加密,也有極高的機率因為對應的順序不同導致需要尋找的次數不一樣。
解密的方式跟加密相當類似,同樣的換法,並且執行密文的次數就能得到原始的字元,而關鍵的解密要用的金鑰就是 Logistic Map 的初始條件跟參數。
Code:
以下的例子是加密一張影像叫 Lena,會先把它轉成一維陣列在開始用此方法。
Encrypt
clear all;
b = 3.999999991;
x = 0.3388;
for i = 1:100
x = b*x*(1-x);
end
lena = imread('lena_small.bmp');
lena = rgb2gray(lena);
lena = reshape(lena, size(lena,1)*size(lena,2),1);
% statistic freq
freq = zeros(256,1);
for i = 1:size(lena,1)
freq(lena(i)+1) = freq(lena(i)+1)+1;
end
% order is the freq order
[B, order] = sort(freq, 'descend');
% copy lena to origin
origin = repmat(lena, 1);
% random permutation
for i = 1:size(lena,1)
x = b*x*(1-x);
index = round(x*size(lena,1));
if(index==0)
index = 1;
end
temp = origin(index);
origin(index) = origin(i);
origin(i) = temp;
end
% encryption and compression
result = zeros(size(lena,1),1);
for i = 1:size(lena,1)
i
temp_order = repmat(origin, 1);
count = 0; % save ciphertext
freq_index = 1;
while(true)
x = b*x*(1-x);
index = round(x*size(lena,1));
if(index==0)
index = 1;
end
count = count + 1;
value = temp_order(index);
if(value==lena(i))
result(i) = count;
break;
end
for j = 1:size(lena,1)
if(temp_order(j)==value)
temp_order(j) = order(freq_index)-1;
end
end
freq_index = freq_index + 1;
if(freq_index>256)
freq_index = 1;
end
end
end 在解密這邊還是讀了 lena 的原因是需要統計他的機率跟弄出那個區塊分割,真實情況應該是這個也當作是金鑰一樣,一起存起來。
Decrypt
clear all;
b = 3.999999991;
x = 0.3388;
% the result of encryption
result = load('result1.mat');
result = result.result;
for i = 1:100
x = b*x*(1-x);
end
lena = imread('lena_small.bmp');
lena = rgb2gray(lena);
lena = reshape(lena, size(lena,1)*size(lena,2),1);
% statistic freq
freq = zeros(256,1);
for i = 1:size(lena,1)
freq(lena(i)+1) = freq(lena(i)+1)+1;
end
% order is the freq order
[B, order] = sort(freq, 'descend');
% copy lena to origin
origin = repmat(lena, 1);
% random permutation
for i = 1:size(lena,1)
x = b*x*(1-x);
index = round(x*size(lena,1));
if(index==0)
index = 1;
end
temp = origin(index);
origin(index) = origin(i);
origin(i) = temp;
end
% decription
output = zeros(size(lena,1),1);
for i = 1:size(lena,1)
i
temp_order = repmat(origin, 1);
count = result(i); % ciphertext means iteration
freq_index = 1;
for k = 1:count
x = b*x*(1-x);
index = round(x*size(lena,1));
if(index==0)
index = 1;
end
value = temp_order(index);
if(k==count)
output(i) = value;
break;
end
for j = 1:size(lena,1)
if(temp_order(j)==value)
temp_order(j) = order(freq_index)-1;
end
end
freq_index = freq_index + 1;
if(freq_index>256)
freq_index = 1;
end
end
end 結果:
這邊的例子是跑一張50*50大小的圖片,換句話說有2500個元素需要加密。
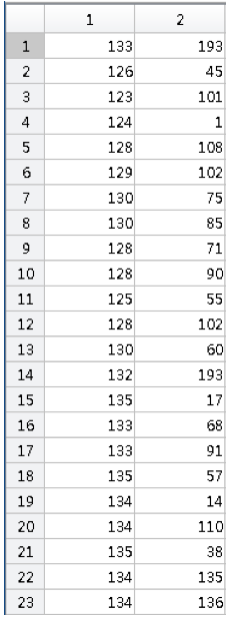
這是擷取前23項的結果,第一行是原始的值,因為是影像,所以可以看附近的值都不會差距太大,第二行是加密過後的結果,有很多個原始值一樣但加密過後的結果不一樣的例子,如第19, 20列。
在 core i7, 16G ram 的電腦上跑,加密跟解密的執行時間都需要5分鐘上下。
Reference:
[1] A Modified Chaos-Based Joint Compression and Encryption Scheme, Jianyong Chen, Junwei Zhou, and Kwok-Wo Wong, Senior Member, IEEE
[2] Embedding Compression in Chaos-Based Cryptography, Kwok-Wo Wong, Senior Member, IEEE, and Ching-Hung Yuen